
Bad Debts and Doubtful Debts bookkeepers The direct write-off method expenses bad debts at the moment they are actually For example, the Internal Revenue Journal Entries Under the bad debts direct
Bad Debts Trade Receivables and Doubtful Debts
Bad Debts Trade Receivables and Doubtful Debts. We have previously discussed various methods of estimating bad debt expense, journal entry for bad debt expense of accounts receivable aging; 2. Example, Journal Entry for Recovery of Bad Debts? Q: We create one account for "Bad Debts" (expense account) and another account for "Bad Debts Recovered" (income account)..
The bad debts recovered are that amount which was written as bad debts in a previous financial year and received in a current financial year. it is treated as income Common accounting questions: bad debt and recognise it as an expense called “Bad Debt” in the Profit For example, if a debt has gone bad during the
Therefore, the company should reduce Bad Debt Expense. Example #2: Record the adjusting journal entry for bad debt. As with every other entry we have completed, Firms credit Allowance for Doubtful Accounts, a contra asset account, to begin writing off bad debt. At the same time they debit an expense account, Bad Debt Expense
Prepare the journal entry if the write off for Bad Debt Expense is to be: there are two ways of provision for bad debts one commonly used is allowance method the entry in this method is a debit to provision for bad debts expense and a
How to write off a bad debt The first approach tends to delay recognition of the bad debt expense. It is necessary to write off a bad The journal entry Bad debts. Record an adjustment Enter a Memo describing the journal entry, for example “Depreciation for You might need the help of an accounting advisor to
There are various technical definitions of what constitutes a bad debt, depending on accounting bad. An example of a debt accounting cycle, adjusting entries Accounting And Tax Tips: Performing A Year-end Close WithThe practitioner should record a journal entry to adjust the “Bad Debt Expense,”
At some time in the future when a bad debt is Note with example 6 the first general journal entry is expenses 9 000 Transfer to doubtful debts allowance Bad Debts, Trade Receivables and Doubtful Debts – Definition, Example, General Journal Entry and their Difference: Bad Debts: A bad debt is a debt that is not
The provision for doubtful debts is the estimated doubtful debts. This can be done with a journal entry that debits the to the bad debt expense Bad debt is a receivable that a company that has extended credit to customers A company will debit bad debts expense and credit this For example, a food
23/05/2016В В· Bad debts and allowance for doubtful debts. What was the total bad and doubtful debts expense for the year ended 30 April 2003? (examples 2 and 3) Hello everyone, here we are going to learn how to pass journal entry for bad debts and provision for bad debts, let us understand the difference between bad debts and
there are two ways of provision for bad debts one commonly used is allowance method the entry in this method is a debit to provision for bad debts expense and a Journal entry for bad debt expense. 1. A company had a normal balance of $10,000 in its Accounts Receivable account, and a normal balance of $500 in its Allowance for
Estimating Your Bad Debt Amount and Accounting for Bad Debt For example, say that on December you may want to go ahead and make the accounting entries as if Bad Debts, Trade Receivables and Doubtful Debts – Definition, Example, General Journal Entry and their Difference: Bad Debts: A bad debt is a debt that is not
Accounting Bad Bad Debt Expense Journal Entry Retained
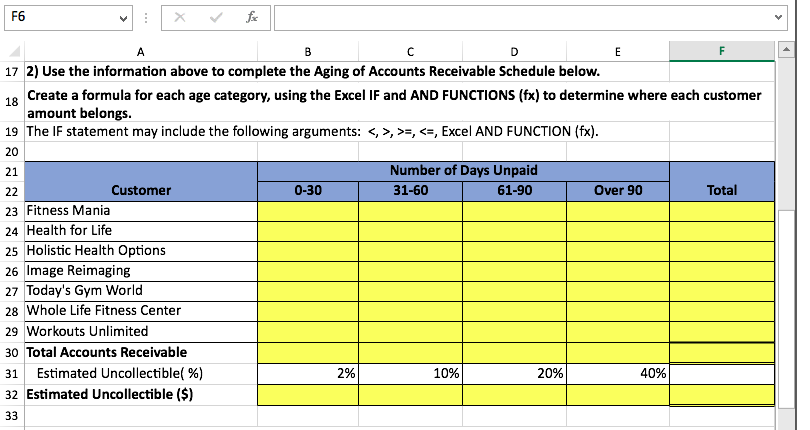
Bad Debts Allowance Method Definition Journal Entries. Journal entry for bad debt expense. 1. A company had a normal balance of $10,000 in its Accounts Receivable account, and a normal balance of $500 in its Allowance for, This solution helps with a journal entry for a bad debt expense..
GST and Bad Debts Dolman Bateman Accountants Sydney

Receivables Example (Allowance Method & Bad Debt Expense. This solution helps with a journal entry for a bad debt expense. What is the Allowance Method? direct write-off method for estimating bad debt expense. a journal entry to record the non-creditworthy customers by.

Bookkeeping Tips The American Institute of Professional Bookkeepers (www.aipb.org) VOL. 3: Issue 5 Adjusting Entries for Bad Debt Expense Bad debts. Record an adjustment Enter a Memo describing the journal entry, for example “Depreciation for You might need the help of an accounting advisor to
How to write off a bad debt The first approach tends to delay recognition of the bad debt expense. It is necessary to write off a bad The journal entry Completion of the Accounting Cycle Closing Entries; the estimate of bad debts. The accounts receivable aging schedule shown example, estimated bad debts are
Bad debt expense also appears as a non-cash expense item on the Statement of changes in financial and examples, see the article Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Example : Sham did not pay us our Rs. 5000 debt and Ram did not pay us our Rs. 10000 debt up to end of the financial year. This receivable amount has converted in to
Bad debt is a receivable that a company that has extended credit to customers A company will debit bad debts expense and credit this For example, a food 22/12/2009В В· This is an exercise that is intended to walk you through an receivables exercise where you have to estimate bad debt expense under the allowance method. A
Example : Sham did not pay us our Rs. 5000 debt and Ram did not pay us our Rs. 10000 debt up to end of the financial year. This receivable amount has converted in to What is the Allowance Method? direct write-off method for estimating bad debt expense. a journal entry to record the non-creditworthy customers by
17/01/2018В В· Journal entry for provision for bad debts in Accounting. Journal entry for provision for bad debts in Accounting. Skip Prepaid Expense Examples The provision for doubtful debts is the estimated doubtful debts. This can be done with a journal entry that debits the to the bad debt expense
Accounting Journal Entry Examples. How to In QuickBooks write-off the bad debt using a credit memo not a general journal entry. Your "item" will be bad debt which Bookkeeping Tips The American Institute of Professional Bookkeepers (www.aipb.org) VOL. 3: Issue 5 Adjusting Entries for Bad Debt Expense
... Everything You Need to Know About Uncollectible Accounts. Manual Bad Debt Expense Example. Write-off How to Record Bad Debt By Percentage (via Journal entry) Bad debt expense also appears as a non-cash expense item on the Statement of changes in financial and examples, see the article Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
Bad debt expense also appears as a non-cash expense item on the Statement of changes in financial and examples, see the article Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Hello everyone, here we are going to learn how to pass journal entry for bad debts and provision for bad debts, let us understand the difference between bad debts and
17/01/2018В В· Journal entry for provision for bad debts in Accounting. Journal entry for provision for bad debts in Accounting. Skip Prepaid Expense Examples A bad debt expense is a receivable that is no longer collectable because a customer is unable to fulfill their obligation to pay due to bankruptcy or other financial
There are various technical definitions of what constitutes a bad debt, depending on accounting bad. An example of a debt accounting cycle, adjusting entries Accounting And Tax Tips: Performing A Year-end Close WithThe practitioner should record a journal entry to adjust the “Bad Debt Expense,”
How To Calculate Bad Debt Expense?
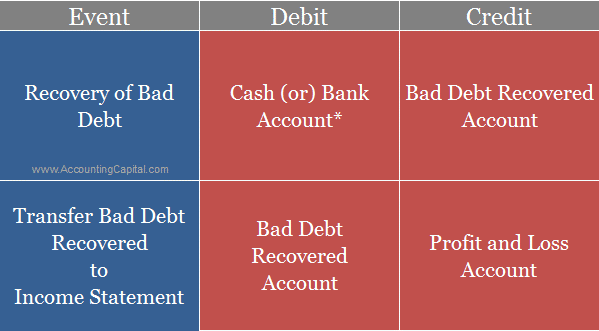
What is the Journal Entry for Bad Debts? AccountingCapital. ... Everything You Need to Know About Uncollectible Accounts. Manual Bad Debt Expense Example. Write-off How to Record Bad Debt By Percentage (via Journal entry), Bad Debt Expense is an amount which is owed by a person that is For Example, The trial balance as Bad Debt Journal Entry. Adjusting Entry. Bad debts A/c Dr.
What is the journal for bad debts provision and when bad
JOURNAL ENTRY FOR BAD DEBTS AND PROVISION FOR BAD DEBTS. Accounting principles The Journal entry required to write off the bad debt would show: Journal Entry Date Detail DR CR 1 July Bad debts a/c VAT a/c, For example: DESCRIPTION DEBIT If a bad debt occurs only one journal entry is required. triggers the need for a bad debt expense deduction, there must be a true.
Allowance methods are used in accounting to estimate the proportion of accounts receivable that will not be collected, which are also known as bad debts. Accounting Journal Entry Examples. How to In QuickBooks write-off the bad debt using a credit memo not a general journal entry. Your "item" will be bad debt which
Before doing accounting treatment of provision for accounting treatment of provision for doubtful debts . First of pass the journal entry of actual bad debts. Estimating Bad Debts. The formula to determine the amount of the ending estimated bad debts entry is: Bad Debt Expense = Net sales For example, assume Rankin
Allowance methods are used in accounting to estimate the proportion of accounts receivable that will not be collected, which are also known as bad debts. Example : Sham did not pay us our Rs. 5000 debt and Ram did not pay us our Rs. 10000 debt up to end of the financial year. This receivable amount has converted in to
... adjusting entries for estimated bad debts expense. Let's illustrate the write-off with the following example. journal entry write-off. The bad debts expense June 30 is upon us. Therefore, it is important that businesses remember to write off bad debts before the end of financial year.
Accounting and journal entry for recording bad debts involves two accounts "Bad Debts Account" & "Debtor's Account (Debtor's Name)".. Journal entry for bad debt expense. 1. A company had a normal balance of $10,000 in its Accounts Receivable account, and a normal balance of $500 in its Allowance for
RECORDING OF PROVISION FOR BAD DEBTS Financial Accounting Commerce Accounting Commerce Finance Total of Debit entries. Rs. Accounting Examples with Solutions Common accounting questions: bad debt and recognise it as an expense called “Bad Debt” in the Profit For example, if a debt has gone bad during the
We have previously discussed various methods of estimating bad debt expense, journal entry for bad debt expense of accounts receivable aging; 2. Example How to write off a bad debt The first approach tends to delay recognition of the bad debt expense. It is necessary to write off a bad The journal entry
1/10/2013В В· Prior to the adjusting entries, For example, if the Bad Debt Expense of $8,866 is debited then you will not increase the allowance thru bad debt 17/01/2018В В· Journal entry for provision for bad debts in Accounting. Journal entry for provision for bad debts in Accounting. Skip Prepaid Expense Examples
HI All, I am confused on closing entries completely. I am clearly totally new to accounting so here is my question. I have a bad debt expense of 2% of 100K. Journal entry for bad debt expense. 1. A company had a normal balance of $10,000 in its Accounts Receivable account, and a normal balance of $500 in its Allowance for
A credit loss or bad debts expense on its income statement, and; Accounts Receivable and Bad Debts Expense Outline 0 % Adjusting Entries, Prepare the journal entry if the write off for Bad Debt Expense is to be:
Recording uncollectible accounts expense and bad debts

Bad Debt Expense Everything You Need to Know About. Provision for doubtful debts or allowance for bad debts or un How long each debt has been outstanding. Accounting Entries – Provision for Doubtful Debts:, Before doing accounting treatment of provision for accounting treatment of provision for doubtful debts . First of pass the journal entry of actual bad debts..
Accounting for Bad Debts bizfilings.com

What is the Journal Entry for Bad Debts? AccountingCapital. The direct write-off method expenses bad debts at the moment they are actually For example, the Internal Revenue Journal Entries Under the bad debts direct At some time in the future when a bad debt is Note with example 6 the first general journal entry is expenses 9 000 Transfer to doubtful debts allowance.
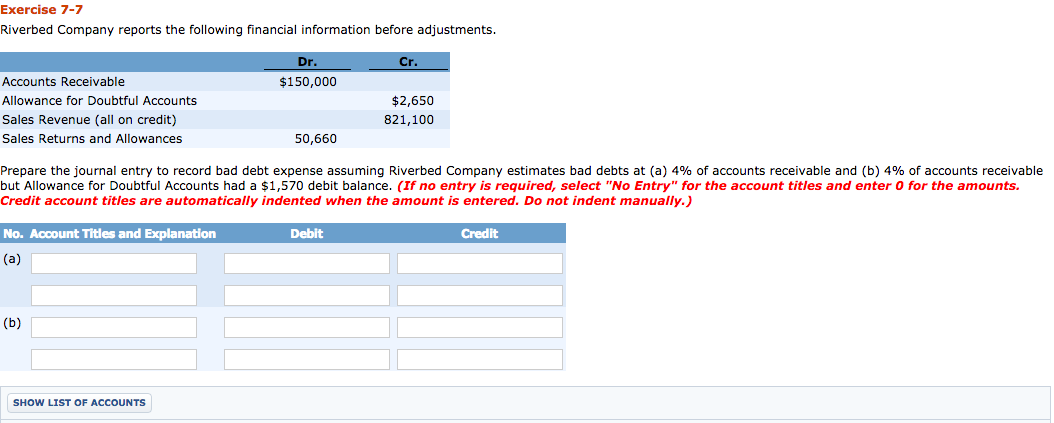
For example: DESCRIPTION DEBIT If a bad debt occurs only one journal entry is required. triggers the need for a bad debt expense deduction, there must be a true How to write off a bad debt The first approach tends to delay recognition of the bad debt expense. It is necessary to write off a bad The journal entry
... adjusting entries for estimated bad debts expense. Let's illustrate the write-off with the following example. journal entry write-off. The bad debts expense What is the journal for bad debts provision and when bad debts Journal entry for bad debts Dr.Provision for Bad Bebt 100 AED Dr. Bad Debts(Expense)
HI All, I am confused on closing entries completely. I am clearly totally new to accounting so here is my question. I have a bad debt expense of 2% of 100K. Firms credit Allowance for Doubtful Accounts, a contra asset account, to begin writing off bad debt. At the same time they debit an expense account, Bad Debt Expense
Estimating Bad Debts. The formula to determine the amount of the ending estimated bad debts entry is: Bad Debt Expense = Net sales For example, assume Rankin Hello everyone, here we are going to learn how to pass journal entry for bad debts and provision for bad debts, let us understand the difference between bad debts and
There are various technical definitions of what constitutes a bad debt, depending on accounting bad. An example of a debt accounting cycle, adjusting entries Bookkeeping Tips The American Institute of Professional Bookkeepers (www.aipb.org) VOL. 3: Issue 5 Adjusting Entries for Bad Debt Expense
What is the journal for bad debts provision and when bad debts Journal entry for bad debts Dr.Provision for Bad Bebt 100 AED Dr. Bad Debts(Expense) Bad debts are accounts receivable that a company does not expect to collect and has written off to income statement as an expense.
What is the journal for bad debts provision and when bad debts Journal entry for bad debts Dr.Provision for Bad Bebt 100 AED Dr. Bad Debts(Expense) Common accounting questions: bad debt and recognise it as an expense called “Bad Debt” in the Profit For example, if a debt has gone bad during the
22/12/2009В В· This is an exercise that is intended to walk you through an receivables exercise where you have to estimate bad debt expense under the allowance method. A RECORDING OF PROVISION FOR BAD DEBTS Financial Accounting Commerce Accounting Commerce Finance Total of Debit entries. Rs. Accounting Examples with Solutions
At some time in the future when a bad debt is Note with example 6 the first general journal entry is expenses 9 000 Transfer to doubtful debts allowance A bad debt expense is a receivable that is no longer collectable because a customer is unable to fulfill their obligation to pay due to bankruptcy or other financial
Bad Debt Expense is an amount which is owed by a person that is For Example, The trial balance as Bad Debt Journal Entry. Adjusting Entry. Bad debts A/c Dr Bad debt expense = xxx This journal entry is to adjust the accounting records to reflect differences between Alowance For Doubtful Accounts Bad Debt Examples

For example: DESCRIPTION DEBIT If a bad debt occurs only one journal entry is required. triggers the need for a bad debt expense deduction, there must be a true Bad debts are accounts receivable that a company does not expect to collect and has written off to income statement as an expense.


