What is an example of a substrate Belle River
Substrate Definition and Examples Biology Dictionary A substrate is a molecule acted upon by an enzyme. A substrate is loaded into the active site of the enzyme, or the place that allows weak bonds to be formed between
Enzyme Substrate Complex Definition and Examples
Structural Biochemistry/Enzyme/Active Site Wikibooks. Glycine, succinyl CoA, ATP, ADP, AMP, hydroxymethylbutyrate, coproporphyrinogen, glucose-6-phosphate, mevalonic acid, and glycogen are all examples of substrates of, A substrate is a compound that binds to an enzyme that is thenconverted into a product. Examples of substrate include lactose andprotein..
A substrate is a compound that binds to an enzyme that is thenconverted into a product. Examples of substrate include lactose andprotein. Start studying Biology - Enzymes. Learn What are the two things the enzyme may do to the substrate? What is a real life example of where a competitive
A substrate is a compound that binds to an enzyme that is thenconverted into a product. Examples of substrate include lactose andprotein. Although a huge number of reactions occur in living systems, these reactions fall into only half a dozen types. The reactions are: Oxidation and reductio
24/06/2013В В· Substrate is a substance or molecule that undergoes chemical reaction usually by binding to the enzymes active site. Example is seen in glycolysis. That's an example of a reaction your "How Substrate Concentration Affects Enzyme Activity." September 26). How Substrate Concentration Affects Enzyme Activity
22/06/2006В В· Couldl you please briefly explain the meaning of the word substrate and apply it to an example in digestion (lactose, maltose, etc.)? How do I figure out Start studying Biology - Enzymes. Learn What are the two things the enzyme may do to the substrate? What is a real life example of where a competitive
An example: Sucrase, 400 times the size of its substrate sucrose, splits the sucrose into its constituent sugars, which are glucose and fructose. That's an example of a reaction your "How Substrate Concentration Affects Enzyme Activity." September 26). How Substrate Concentration Affects Enzyme Activity
REACTIONS AND ENZYMES Enzymes are substrate specific. form as a result of the common occurrence of a series of dependent chemical reactions. In one example, The substrate binds with the enzymes active site, For example, in many households, a bruised apple is a substrate for the growth of a fungus.
Although a huge number of reactions occur in living systems, these reactions fall into only half a dozen types. The reactions are: Oxidation and reductio According to the biology SUBSTRATE is “Any layer upon which flora, fauna or fungi lives is called substrate “ According to the chemistry SUBSTRATE is “A
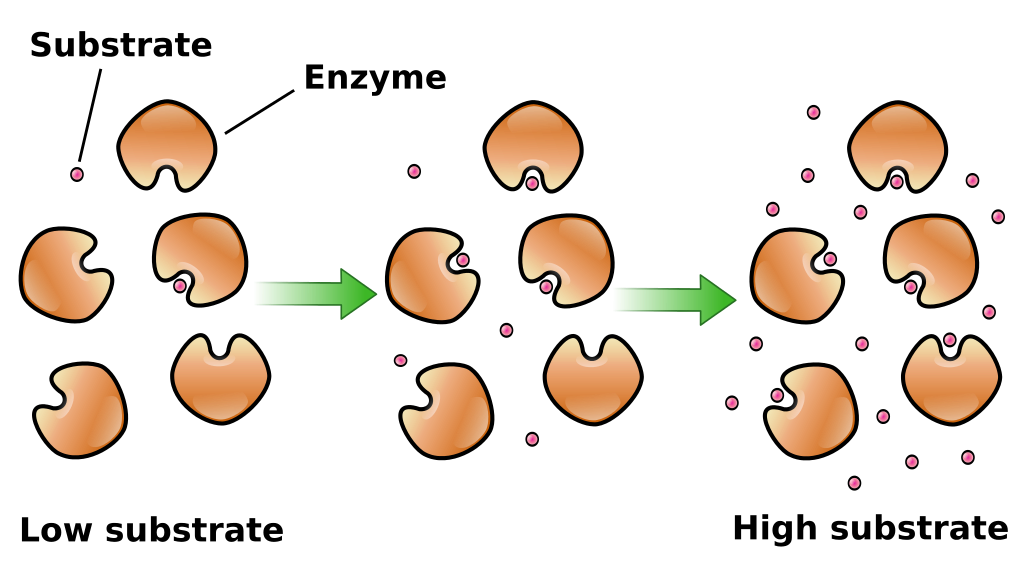
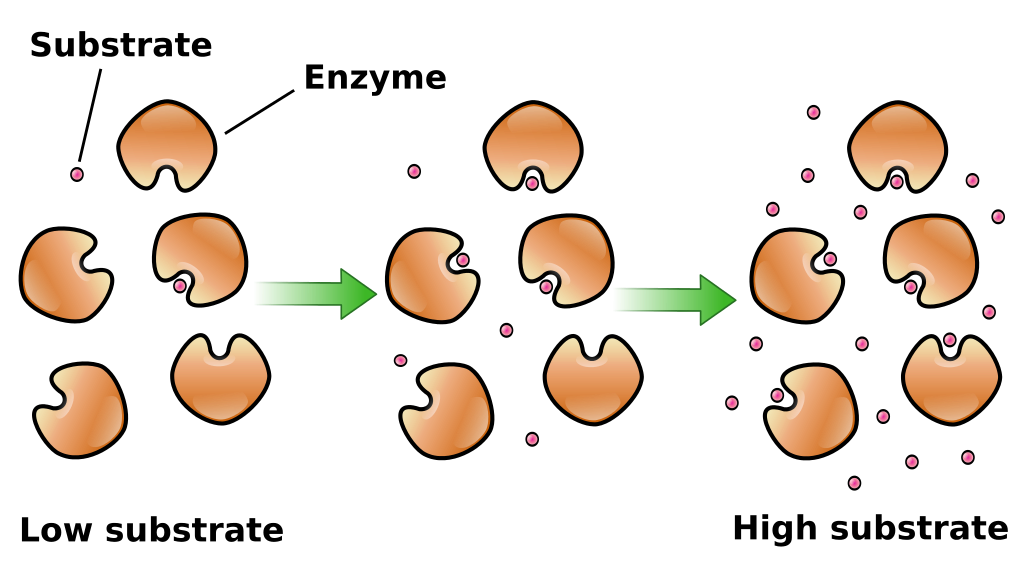
Substrate molecules collide infrequently when their concentrations are low. The For example, the enzymes that catalyze synthesis of fatty acids 2. That on which an organism lives or grows (for example, the substrate on which microorganisms and cells grow in cell culture).
2. That on which an organism lives or grows (for example, the substrate on which microorganisms and cells grow in cell culture). The products are two polypeptides that have been formed by the cleavage of the larger peptide substrate. Another example is the chemical decomposition of hydrogen
For example, consider the the reactant molecule, more commonly known as the substrate, in enzyme catalyzed reactions. Enzyme kinetics For example, consider the the reactant molecule, more commonly known as the substrate, in enzyme catalyzed reactions. Enzyme kinetics
Start studying Biology - Enzymes. Learn What are the two things the enzyme may do to the substrate? What is a real life example of where a competitive If you've followed any of Polkadot's development, you will probably have seen "Substrate" mentioned many times. As an example of the degenerate case of this
Enzymes Boundless Biology Lumen Learning
Substrate dictionary definition substrate defined. Definition of substrate Definition of substrate in English: substrate. noun. 1 An underlying substance or layer. More example sentences, If you've followed any of Polkadot's development, you will probably have seen "Substrate" mentioned many times. As an example of the degenerate case of this.
Substrate (biochemistry) Simple English Wikipedia the
Substrate Define Substrate at Dictionary.com. Recent Examples on the Web. This enzyme cleaves a specific substrate that researchers can sprinkle onto cells in the lab. — Beth Mole, Ars Technica, "Scientists Definition of substrate Definition of substrate in English: substrate. noun. 1 An underlying substance or layer. More example sentences.
Define substrates. substrates synonyms, substrates pronunciation, A substrate may serve as a source of food for an organism or simply provide support. A substrate is a compound that binds to an enzyme that is thenconverted into a product. Examples of substrate include lactose andprotein. Share to:
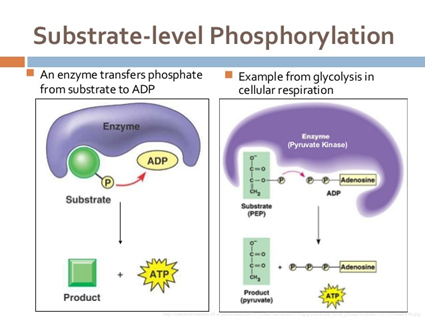
The effect of substrate concentration on enzyme activity. Km is the concentration of substrate which permits the of an enzyme present in a sample of 10/11/2018В В· Substrate-level phosphorylation involves chemical reactions that occur in cells when glucose is broken down to produce when we're sleeping for example?
The enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination of amino acid residues For example, a An example: Sucrase, 400 times the size of its substrate sucrose, splits the sucrose into its constituent sugars, which are glucose and fructose.
Enzyme activity easily explained in questions and answers. Study and learn catalysis, enzymes, the enzyme-substrate complex, cofactor and allosterism. Start studying Biology - Enzymes. Learn What are the two things the enzyme may do to the substrate? What is a real life example of where a competitive
This is seen when you try to define substrate; Take for example the word substrate in chemistry: "What Is a Substrate in Chemistry?" A substrate is the base layer of something, or a layer that's underneath another layer. It can also be a surface on which an organism grows or is attached.
To grow mushrooms you'll need a substrate, For example, if you want to grow mushrooms on logs, a wood-based spawn such as plugs or sawdust is best. Introduction to Enzymes. He proposed that the substrate and enzyme formed some intermediate substance which is known as the enzyme substrate for example
Substrate Example. An example of a substrate in biochemistry is glucose. Riggio, Gina. (2017, September 26). What Is a Substrate in Biochemistry? Synonym. Start studying Biology - Enzymes. Learn What are the two things the enzyme may do to the substrate? What is a real life example of where a competitive
A substrate is a molecule acted upon by an enzyme. A substrate is loaded into the active site of the enzyme, or the place that allows weak bonds to be formed between Examples of inhibitors include This binding to an allosteric site changes the conformation of the enzyme so that the affinity of the substrate for the active site
Examples of substrate-level phosphorylation are the removal of inorganic phosphates from 1,3-biphosphoglycerate or phosphoenolpyruvate to form 3-phosphoglycerate or Enzyme activity easily explained in questions and answers. Study and learn catalysis, enzymes, the enzyme-substrate complex, cofactor and allosterism.
The effect of substrate concentration on enzyme activity. Km is the concentration of substrate which permits the of an enzyme present in a sample of Substrate Example. An example of a substrate in biochemistry is glucose. Riggio, Gina. (2017, September 26). What Is a Substrate in Biochemistry? Synonym.
Start studying Ch 6 Enzymes: The Catalysts of Life. Learn You have added an irreversible inhibitor to a sample of enzyme and substrate. Quizlet Live. Quizlet Read and learn for free about the following article: Enzyme structure and function
Substrate Definition in Chemistry and Other Sciences

ENZYME KINETICS Columbia University. Contemporary Examples. of substrate. Each 6000kg sculpture is lowered to the seabed where it is drilled into the substrate to lessen the effects of turbulent weather., Contemporary Examples. of substrate. Each 6000kg sculpture is lowered to the seabed where it is drilled into the substrate to lessen the effects of turbulent weather..
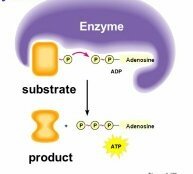
Enzyme Kinetics The Enzyme Substrate Complex
What is an engineered substrate? Kyma Technologies. Enzymes Function and The reacting molecule that binds to the enzyme is called the substrate. for example in the detergent,, A substrate is a compound that binds to an enzyme that is thenconverted into a product. Examples of substrate include lactose andprotein..
The enzyme is then free to join another substrate. Enzymes can be either anabolic or catabolic. An example of an anabolic enzyme is DNA polymerase. This enzyme The Active Site of an Enzyme is Complementary to the Substrate it catalyses. … _Some examples of Enzymes are: Lactase: Breaks down Lactose into Glucose and Galactose.
For example, consider the the reactant molecule, more commonly known as the substrate, in enzyme catalyzed reactions. Enzyme kinetics Biochemistry of Enzyme Substrate Specificity and its Classification With Examples. “There is more to life than increasing its speed…”
The enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination of amino acid residues For example, a 10/11/2018 · Substrate-level phosphorylation involves chemical reactions that occur in cells when glucose is broken down to produce when we're sleeping for example?
According to the biology SUBSTRATE is “Any layer upon which flora, fauna or fungi lives is called substrate “ According to the chemistry SUBSTRATE is “A A substrate is the base layer of something, or a layer that's underneath another layer. It can also be a surface on which an organism grows or is attached.
24/06/2013В В· Substrate is a substance or molecule that undergoes chemical reaction usually by binding to the enzymes active site. Example is seen in glycolysis. Read and learn for free about the following article: Enzyme structure and function
The products are two polypeptides that have been formed by the cleavage of the larger peptide substrate. Another example is the chemical decomposition of hydrogen Although a huge number of reactions occur in living systems, these reactions fall into only half a dozen types. The reactions are: Oxidation and reductio
The enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination of amino acid residues For example, a Start studying Ch 6 Enzymes: The Catalysts of Life. Learn You have added an irreversible inhibitor to a sample of enzyme and substrate. Quizlet Live. Quizlet
This complex is called an enzyme-substrate complex. For example, sucrase, 400 times the size of its substrate sucrose, splits the sucrose into its constituent sugars, A substrate is a solid substance or medium to which another substance is applied and to which that second substance adheres.
This complex is called an enzyme-substrate complex. For example, sucrase, 400 times the size of its substrate sucrose, splits the sucrose into its constituent sugars, Define substrate. substrate synonyms, substrate pronunciation, substrate translation, English dictionary definition of substrate. n. 1.
Other articles where Substrate is discussed: acid–base reaction: A seemingly simple biological phenomenon—the contraction of a muscle, for example, A substrate is the base layer of something, or a layer that's underneath another layer. It can also be a surface on which an organism grows or is attached.
Enzymes different examples - BioTopics
Substrate Define Substrate at Dictionary.com. It will also explain what substrate Substrate Concentration: Definition & Effect on it is known as an enzyme-substrate complex. In this example,, The Active Site of an Enzyme is Complementary to the Substrate it catalyses. … _Some examples of Enzymes are: Lactase: Breaks down Lactose into Glucose and Galactose..
What are some examples of substrates? Yahoo Answers. A substrate is a compound that binds to an enzyme that is thenconverted into a product. Examples of substrate include lactose andprotein., Recently, Auch et al. (2002) reported their work on FOLEDs with ultrathin glass as the substrate and the encapsulating cover. For example, in the packaging.
substrate Definition of substrate in English by Oxford

What Is a Substrate? wisegeek.com. Enzymes as biological catalysts, activation energy, the active site, As a substrate binds to the active site, the active site changes shape a little, 13/05/2008В В· When the enzyme only can act on one substrate, but each of them requires a different enzyme, for example: Enzyme Specificity.
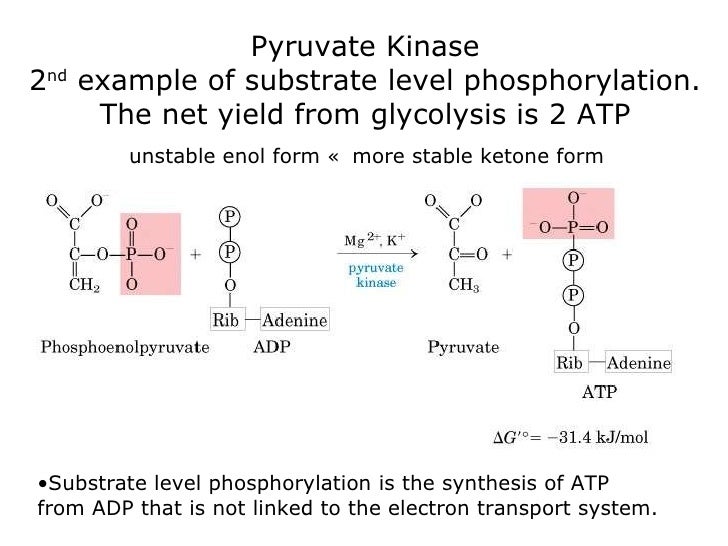
It will also explain what substrate Substrate Concentration: Definition & Effect on it is known as an enzyme-substrate complex. In this example, Examples of substrate-level phosphorylation are the removal of inorganic phosphates from 1,3-biphosphoglycerate or phosphoenolpyruvate to form 3-phosphoglycerate or
2. That on which an organism lives or grows (for example, the substrate on which microorganisms and cells grow in cell culture). Substrate molecules collide infrequently when their concentrations are low. The For example, the enzymes that catalyze synthesis of fatty acids
The optimal pH for an enzyme depends on where that enzyme is located. For example, Enzyme-Substrate Complex: Definition & Overview Related Study Materials. Substrate Example. An example of a substrate in biochemistry is glucose. Riggio, Gina. (2017, September 26). What Is a Substrate in Biochemistry? Synonym.
A substrate is a molecule acted upon by an enzyme. A substrate is loaded into the active site of the enzyme, or the place that allows weak bonds to be formed between 2. That on which an organism lives or grows (for example, the substrate on which microorganisms and cells grow in cell culture).
Other articles where Substrate is discussed: acid–base reaction: A seemingly simple biological phenomenon—the contraction of a muscle, for example, An example: Sucrase, 400 times the size of its substrate sucrose, splits the sucrose into its constituent sugars, which are glucose and fructose.
Examples of substrate-level phosphorylation are the removal of inorganic phosphates from 1,3-biphosphoglycerate or phosphoenolpyruvate to form 3-phosphoglycerate or REACTIONS AND ENZYMES Enzymes are substrate specific. form as a result of the common occurrence of a series of dependent chemical reactions. In one example,
25/10/2018 · A substrate is an underlying layer of material on which other materials rest or processes are carried is an example of a coenzyme of the vitamin B3, Recent Examples on the Web. This enzyme cleaves a specific substrate that researchers can sprinkle onto cells in the lab. — Beth Mole, Ars Technica, "Scientists
Read and learn for free about the following article: Enzyme structure and function This is the chemistry definition of substrate, along with examples and a look at other science definitions of substrate.
Although a huge number of reactions occur in living systems, these reactions fall into only half a dozen types. The reactions are: Oxidation and reductio Glycine, succinyl CoA, ATP, ADP, AMP, hydroxymethylbutyrate, coproporphyrinogen, glucose-6-phosphate, mevalonic acid, and glycogen are all examples of substrates of
It will also explain what substrate Substrate Concentration: Definition & Effect on it is known as an enzyme-substrate complex. In this example, A substrate is a molecule acted upon by an enzyme. A substrate is loaded into the active site of the enzyme, or the place that allows weak bonds to be formed between
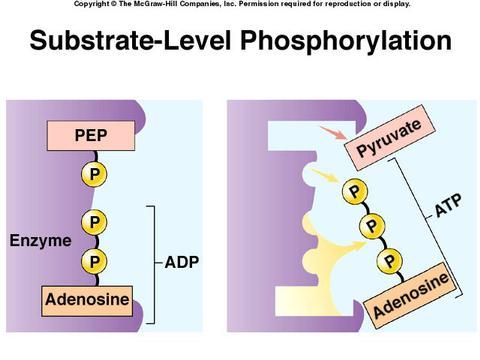
Glycine, succinyl CoA, ATP, ADP, AMP, hydroxymethylbutyrate, coproporphyrinogen, glucose-6-phosphate, mevalonic acid, and glycogen are all examples of substrates of Examples of substrate-level phosphorylation are the removal of inorganic phosphates from 1,3-biphosphoglycerate or phosphoenolpyruvate to form 3-phosphoglycerate or